Flight Radar 24 website is offering free premium accounts for contributing members. You can either ask for free device (if you live in the location where they miss data) or build your own feeder based on RaspberryPi device.
Recommended device is version 3B+, which when adding chassis power supply and SD card is coming around 60USD plus…
I wanted to see if I can get similar device working with FR24FEED for cheaper than that.
Decided to give Debian powered Dell Wyse 3040 Thin Client a go. Reasons:
- Price 🙂 got used one in pristine state for equivalent of 21USD delivered
- Power Efficiency Designed for low power consumption, ideal for battery-operated devices.
- Quad-Core Performance Four cores provide decent multi-threaded performance for casual computing tasks.
- Plenty of USB slots
- and 64bit architecture
Typical Power Consumption for Wyse 3040
State / Power Consumption
- Idle Approx. 6W
- Average Use Approx. 10-12W
- Maximum Up to 15W
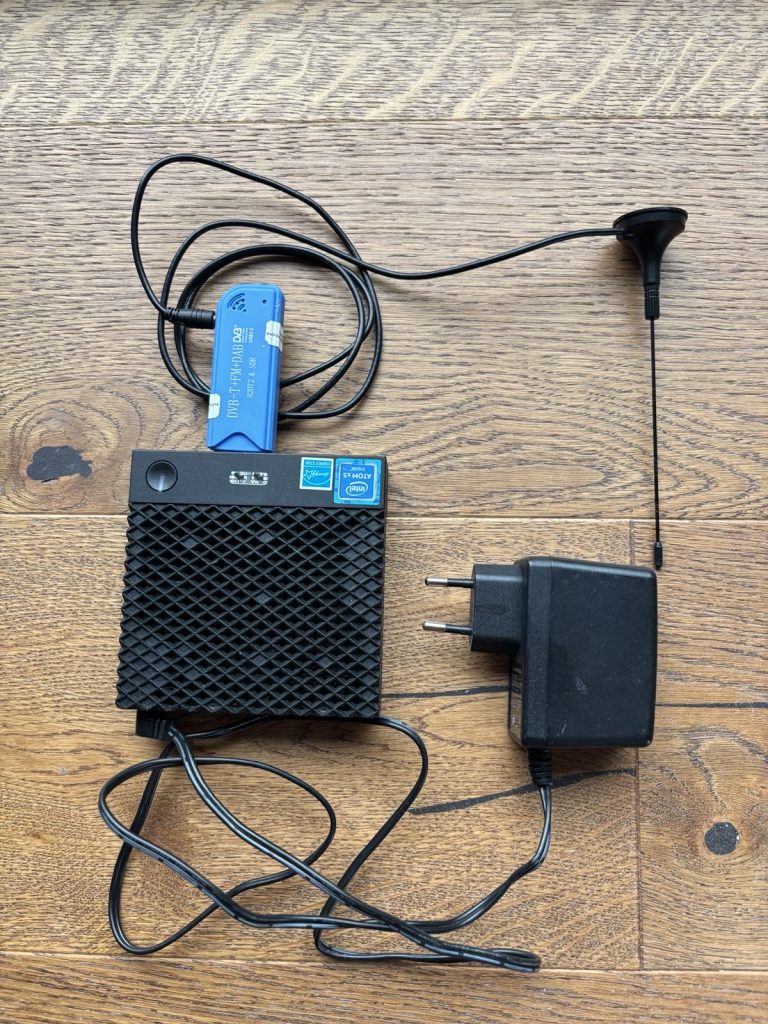
Apart of server you also need device that will fetch radio waves, I used DVB-T – USB dongle based on RTL2832U. Interestingly enough, this part is actually more expensive that Wyse device itself, currently around 35USD on my local online market. If you are willing to wait and get it off Aliexpress, you can find these much cheaper. But I had one lying around so no cost from this project’s perspective.
Final Hardware Spec
- Intel(R) Atom(TM) x5-Z8350 CPU @ 1.44GHz
- 2GB RAM
- 8GB embedded MultiMediaCard (eMMC)
- DVB-T – USB dongle based on RTL2832U
Unfortunately steps for Raspberry listed on Flight Radar website don’t work for amd64 Debian machine due to the fact that dump1060 binary used in script is targeting Raspberry Pi CPU architecture and not amd64. That’s fine – we can download code and built suitable binary ourselves.
Steps taken
- Download minimal Debian iso – at the time of writing it’s Debian 13 Trixie
https://www.debian.org/CD/netinst/debian-13.1.0-amd64-netinst.iso
- use your favorite program to prepere bootable USB stick using downloaded ISO
- Power on Wyse and enter BIOS settings. For me pressing F1 and F2 worked.
- BIOS settings: power status after power loss – Always on + enable boot from USB
- Boot from Debian install USB stick, pressing F12 during power up sequence.
- Follow the flow to install minimal Debian in text mode. Only SSH service is needed.
- I used LVM based partitioning layout. After install you should end up with around 50% of the space of root disk used.
- Reboot, make sure you can system boots okay and gets IP address.
From this moment on you can carry on with installation from other device by ssh’ing onto IP address of your feeder. Once connected via SSH download and execute install script. Good idea to download a copy first and review it before executing with root privileges…
wget -qO- https://fr24.com/install.sh | sudo bash -sYou will be prompted to provide your email address. Make sure to use same address that you use with your free Flight Radar account
Once FR24FEED wizard flow is completed don’t start service just yet. Install required packages, clone code, compile library and copy onto required path:
apt-get install git build-essential fakeroot debhelper librtlsdr-dev pkg-config libncurses5-dev libbladerf-dev libhackrf-dev liblimesuite-dev libsoapysdr-dev devscripts
git clone https://github.com/flightaware/dump1090.git
cd dump1090/
make RTLSDR=yes
cp dump1090 /usr/lib/fr24/
/usr/lib/fr24/dump1090 --version
/usr/lib/fr24/dump1090 --interactiveIf above commands succeeded and you are able to connect to DVB-T stick and see data coming through – you are good to go to start service.
systemctl enable --now fr24feedNow you can review status of your feeder by navigating with your web browser to local IP address of your feeder, port 8754
http://10.0.1.191:8754/

After few hours your free account on Flight Radar 24 will change status to Business – and you start can enjoy using all features.
Bonus content – Ansible playbook for extra steps required
---
- name: Install dump1090 and setup fr24feed
hosts: all
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install required packages
apt:
name:
- git
- build-essential
- fakeroot
- debhelper
- librtlsdr-dev
- pkg-config
- libncurses5-dev
- libbladerf-dev
- libhackrf-dev
- liblimesuite-dev
- libsoapysdr-dev
- devscripts
state: present
update_cache: yes
- name: Clone dump1090 repository
git:
repo: 'https://github.com/flightaware/dump1090.git'
dest: '/opt/dump1090'
- name: Compile dump1090
command: make RTLSDR=yes
args:
chdir: '/opt/dump1090'
- name: Copy dump1090 binary to the specified directory
command: cp dump1090 /usr/lib/fr24/
args:
chdir: '/opt/dump1090'
- name: Check dump1090 version
command: /usr/lib/fr24/dump1090 --version
register: dump1090_version_output
- name: Display dump1090 version
debug:
var: dump1090_version_output.stdout
- name: Run dump1090 in interactive mode
async: 1
poll: 0
command: /usr/lib/fr24/dump1090 --interactive
- name: Enable and start fr24feed service
systemd:
name: fr24feed
enabled: yes
state: started